A medical device is any instrument, apparatus, implement, machine, appliance, implant, reagent for in vitro use, software, material, or other similar or related article intended by the manufacturer to be used, alone or in combination, for human beings for one or more of the following specific medical purposes:
- Diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment, or alleviation of disease.
- Diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, alleviation, or compensation for an injury.
- Investigation, replacement, modification, or support of the anatomy or of a physiological process.
- Supporting or sustaining life.
- Control of conception.
- Disinfection of medical devices.
- Providing information by means of in vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body.
- Medical devices range from simple tools like tongue depressors and bandages to complex machinery like MRI machines and heart-lung machines. They also include diagnostic devices such as
- blood glucose meters, therapeutic devices like pacemakers, and life-support devices like ventilators.
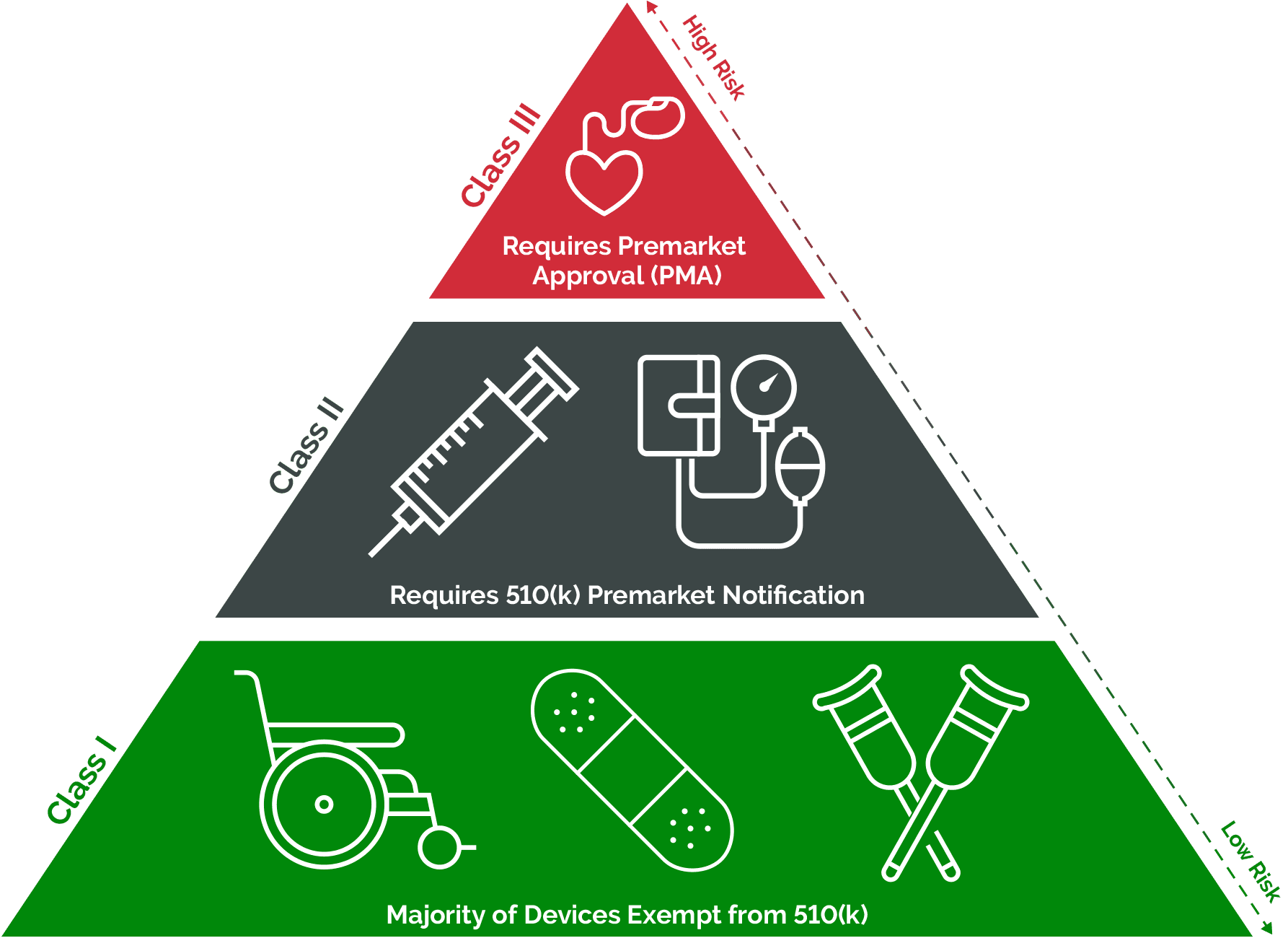
The regulation of medical devices ensures their safety and efficacy. This involves pre-market approval, post-market surveillance, and adherence to quality standards, typically overseen by regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA).